Input and Output Devices of Computer
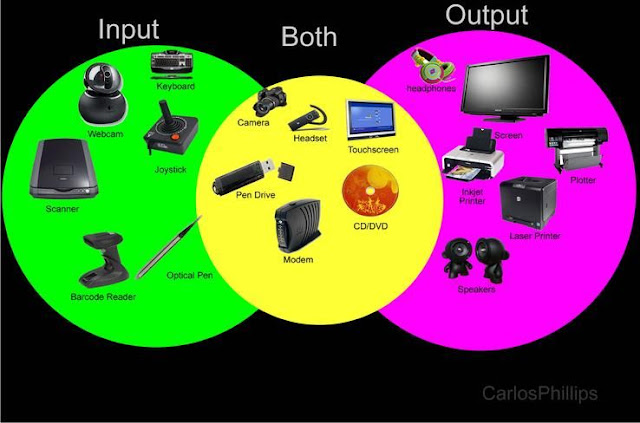
Input Devices:
In computing, an input device is a piece of computer
hardware equipment used to provide data and control signals to an information
processing system such as a computer or information appliance. Examples of
input devices include keyboards, mouse, scanners, digital cameras and
joysticks. Audio input devices may be used for purposes including speech
recognition.
- Keyboards:
'Keyboards' are a human interface device which
is represented as a layout of buttons.
- Mouse:
Pointing devices are the most
commonly used input devices today. A pointing device is any human interface
device that allows a user to input spatial data to a computer.
- Video Input Devices:
Video input devices are used to digitize
images or video from the outside world into the computer. The information can
be stored in a multitude of formats depending on the user's requirement.
Examples of types
of a video input devices include:
- · Digital camera
- · Digital camcorder
- · Portable media player
- · Webcam
- · Microsoft Kinect Sensor
- · Image scanner
- · Fingerprint scanner
- · Barcode reader
- · 3D scanner
- · Laser rangefinder
- · Eye gaze tracker
- · Computed tomography
- · Magnetic resonance imaging
- · Positron emission tomography
- · Medical ultrasonography
- Audio Devices:
Audio input devices are used to capture sound. In
some cases, an audio output device can be used as an input device, in order to
capture produced sound. Audio input devices allow a user to send audio signals
to a computer for processing, recording, or carrying out commands. Devices such
as microphones allow users to speak to the computer in order to record a voice
message or navigate software. Aside from recording, audio input devices are
also used with speech recognition software.
Examples of types of audio input devices include:
- Microphones
- MIDI keyboard or other digital musical instrument
- Others:
- Gesture recognition
- Digital pen
- Magnetic ink character recognition
- Sip-and-puff#Computer input device
Output devices:
An output device is any piece of computer hardware
equipment which converts the electronically generated information into
human-readable form.
In brief, output unit is responsible for providing
the output in user readable form. It can be text, graphics, tactile, audio, and
video.
Some of the Output devices are Visual Display Units
(VDU) i.e. a Monitor, Printer, Graphic Output devices, Plotters, Speakers etc.
A new type of Output device is been developed these days, known as
Speech synthesizer, a mechanism
attached to the computer which produces verbal output
sounding almost like human speeches.
Display devices:
Since the beginning of the computer history &
evolution we always have seen a sort of display device on the computer. A
display device is the most common form of output device. It presents output
visually on computer screen. The output appears temporarily on the screen and
can easily altered or erased, it is sometimes referred to as soft copy also.
The display device for a desktop PC is called Monitor.
With all-in-one PCs, notebook computers, hand held
PCs and other devices; the term display screen is used for the display device.
The display devices are also used in home entertainment systems, mobile
systems, cameras and video games.
Display devices form images by lighting up the
proper configurations of pixels. In short the display devices are organized in
the form of Pixels, & pixels are arranged in the form of Matrix, a
2-dimensional matrix which is organized as rows & columns.
How Does a Computer Process Data?
Before data is processed by a computer, it has to be
fed into the computer using a keyboard, mouse or another input device. The
central processing unit (CPU) analyzes the raw data and processes it into
sensible information. The CPU receives instructions from the user and issues
prompts accordingly. After the data is processed, it is translated to output
formats that are easily understandable by the user.
The processed data is displayed on the computer for
editing, viewing or playing. The computer’s CPU then receives instructions from
the user to save the data securely on the hard drive. Later, the user can
choose to modify, copy, move, edit or delete the data. Some of the output
values that data is converted into are documents, video files and audio files.
A computer system is comprised of three main parts:
hardware, software and users. All components connected to the computer via
cable or wireless access point are hardware. These are primarily the tangible
parts that include the CPU, monitor, keyboard and mouse. In addition, machines
such as printers and scanners are considered part of the computer's hardware.
Software consists of the computer applications installed on the computer and
used to execute functions. Users are the people who provide instructions to the
computer.
Different Types of Computers Around the World:
There are Four Different Computer Types
We
have four different computer types classified according to their performance,
power, and size. A computer is an electronic device that accepts data,
processes it, stores, and then produces an output.
There
are different computer types available depending on the number of users they
can support at any one time, their size, and power. In this hub, we are going to
have a look at the difference
between
supercomputers, mainframe, mini, and microcomputers.
Supercomputers
Supercomputers
are Very Fast and Most Powerful
1. Supercomputers – Supercomputers are
very expensive, very fast, and the most powerful computers we have in the
world.
Supercomputers
are optimized to execute a few numbers of programs. This makes it possible for
them to execute these few programs at a very high speed. Due to their
inhibiting cost, they are used in high end places like in scientific research
centers. The supercomputer consists of thousands of processors making it clock
very high speeds measured by petaflops.
These
computer types are also very large in size due to the numerous parts and
components involved in their design.
A
good example of a Supercomputer is Tianhe-2: TH-IVB-FEP Cluster; National Super
Computer Center in Guangzhou, China; 3.1
Mainframe Computers
2. Mainframe computers —
These are large and expensive computer types capable of supporting hundreds, or
even thousands, of users simultaneously. Thus, they are mostly used by
governments and large organizations for bulk data processing, critical
applications, transaction processing, census, industry and consumer statistics
among others. They are ranked below supercomputers.
Minicomputers
3. Minicomputers — Minicomputers are mid-sized computers. In terms of size
and power, minicomputers are ranked below mainframes. A minicomputer is a
multiprocessing system capable of supporting from 4 to about 200 users
simultaneously.
Microcomputers
4. Microcomputers or
Personal computers – A personal computer is a computer
designed to be used by one user at a time. The term microcomputer relates to
microprocessor which is used with a personal computer for the purpose of
processing data and instruction codes. These are the most common computer types
since they are not very expensive.
Microcomputers Are Classified as Desktop and Portable (Mobile) Computers
Desktop Computers
Desktop computers are not built to
be mobile. They are moved, but only to a new desktop location and with the power
supply inactive. There are a number of major differences between computers that
are intended to be used in one place as a desktop and portables or mobiles that
can be easily moved from one location to another.
Desktop computers are large and
heavy in comparison to portables. They can be carried in specially manufactured
cases, but only to assist a support engineer in moving, not as a frequent
procedure. The monitor, keyboard and mouse are all separate items on a desktop.
Desktop computer components and
devices, although quite resilient to movement while active are not made to be
constantly moved, even less so when they are operational. A mains power supply
is mandatory, as desktop computers cannot work without a constant supply of
electrical power.
The desktops can further be
subdivided depending with the casing type, tower casing and desktop casing.
Tower casing
For tower casing, the motherboard is
placed on side of the system unit, while the other major components like the
power supply, and mass storage devices are stacked on top of each other in a
cabinet. One main advantage with computers using the tower casings is that
there is ample space for future upgrades for example if you wish to add more
storage devices.
A Mid Tower Case
Desktop casing
For the desktop casings, the
motherboard lies on the bottom and is parallel to the desk or table. The system
unit is usually smaller and more compact. It is not a very good choice if you
are going to install other drives like another hard disk or a DVD writer. One
main advantage is that they are small and thus will occupy less space. The
placement is also ideal since it will lie on top of a desk and then you can
place your TFT monitor on top.
Tower or Desktop
Computer?
Note: You can flip over the tower casing and end up with a
desktop and you can turn your desktop to a tower literally though but the
problem will be your drives will be facing sideways. So you will always have a
problem inserting or removing your CDs because they will keep on falling, other
drives might fail to access your CD or DVD contents due to the awkward tilted
position.
Why
choose a desktop?
The size of the casing determines
how much space you need on your desk to place the PC. If you have a small desk
with limited space, you might consider the smaller minicomputer case.
There are two things that may make
you consider going for tower:
a) If you have more than enough
space is not an issue, then you can go for the tower casing where there are
more functions.
b) If you will be adding a lot of
devices to your system, for example more drives.
In terms of cost, tower casings
prices are a little bit higher compared to desktops.
Portable or Mobile Computers
Portable or mobile computers are
manufactured with a very important feature; they are portable (are designed for
mobility). This means a computer user can be able to move with it from one
point to another comfortably. One can also work from any location irrespective
of if there is a power source. They:
- Are small, compact and light in weight
- Have their own power in form of a battery but of course it does not last forever, thus they have to be plugged to a source of power once in a while.
These portable devices are produced
in a variety of sizes and very high processing capabilities. Good examples are
Laptops, Palmtops, and PDAs.
An Example of the Portable Computers














Comments
Post a Comment